

The founder of Shenzhen Tianmu New Energy Co., Ltd (hereinafter referred to as "Tianmu") and Professor Zhang Jiaheng from the Novelty Laboratory of Harbin Institute of Technology (Harbin IIT), has made important research progress in the field of eutectic electrolytes, ACS Nano", "Nano-Micro Letters" and "Small" and other top international journals.
Lithium-ion batteries have been widely used in all aspects of human life, such as electric vehicles, portable electronics and grid storage stations. With the rapid development of society, the demand for higher energy density of batteries is increasing. However, conventional lithium-ion batteries based on graphite anodes (theoretical capacity 372 mAh g-1) can hardly meet the demand for higher and higher energy densities. New battery chemistries therefore need to be developed, and it is now generally accepted that lithium metal batteries offer a promising solution to the energy density anxiety, since lithium metal has the lowest redox potential (-3.04 V compared to standard hydrogen electrodes) and a high theoretical capacity (3860 mAh g-1). However, the growth of lithium dendrites and unstable solid electrolyte interfacial layers in lithium-metal batteries hinder the development of high energy density lithium-metal batteries. At the same time, the low thermal stability and flammability of most commercial organocarbonate electrolytes currently in use are the main causes of spontaneous combustion and even explosion in lithium-ion batteries. Therefore, it is urgent to design and develop new electrolytes that are both non-flammable and inhibit the growth of lithium dendrites to facilitate the development of the next generation of high safety and high energy density lithium metal batteries. Team Tianmu has carried out corresponding R&D work to address the current electrolyte pain points, as follows:
01 Introduction of lithium nitrate
Lithium nitrate is widely used as an additive in electrolytes to regulate the interfacial film of solid electrolytes, but its application in lithium metal batteries is limited by the extremely low solubility of conventional carbonate electrolytes. Professor Jiaheng Zhang's team has used the strong interaction forces in eutectic molecules to improve the solubility of lithium nitrate in eutectic electrolytes to form non-flammable and safe electrolytes (Figure 1). It was also applied to a variety of high energy density ternary cathode lithium metal batteries to inhibit the formation of lithium dendrites and demonstrate long-lasting and stable cycling performance. The research results were published in the top international journal Advanced Energy Materials (impact factor 29.70), with Yixhong Liang, a PhD student at HUST, and Wanbao Wu, a PhD student at HUST, co-founder of Tianmu and chief R&D officer of Tianmu, as co-authors of the paper.
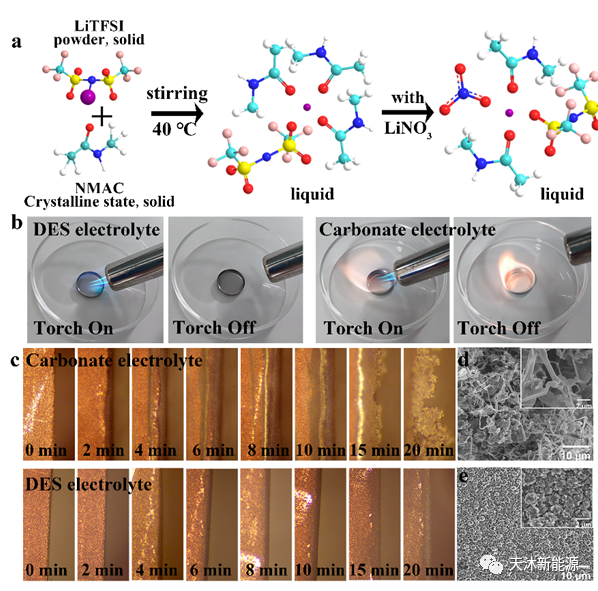
02 Development of high-safety eutectic electrolytes
Although eutectic electrolytes are highly thermally stable and non-flammable, they still suffer from high viscosity and poor compatibility with lithium metals. Professor Jiaheng Zhang's team has designed and developed a non-flammable eutectic electrolyte, while introducing fluorinated ethers as co-solvent to reduce the viscosity of the electrolyte and improve its compatibility with lithium metal. This safe electrolyte facilitates the deposition of spherical lithium without dendrite growth (Figure 2); and when applied to lithium metal batteries with lithium iron phosphate and lithium manganate as cathodes, stable cycling performance can be achieved at room temperature and high temperature of 60°C. This study provides a new perspective on the development of eutectic electrolytes in lithium metal batteries. The related research results were published in the top international journal Nano-Micro Letters (impact factor 23.66), and Wu Wanbao, a PhD student from HUST, co-founder of Tianmu and chief R&D of Tianmu, is the first author of the paper.
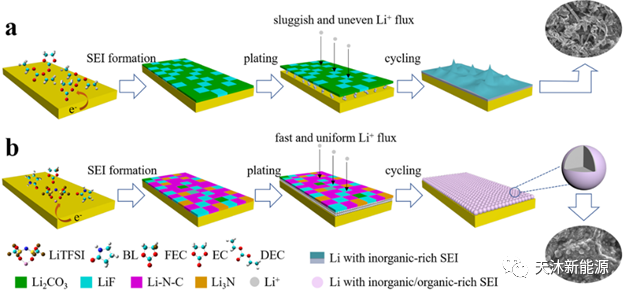
03 Provide new ideas for developing ternary eutectic electrolytes
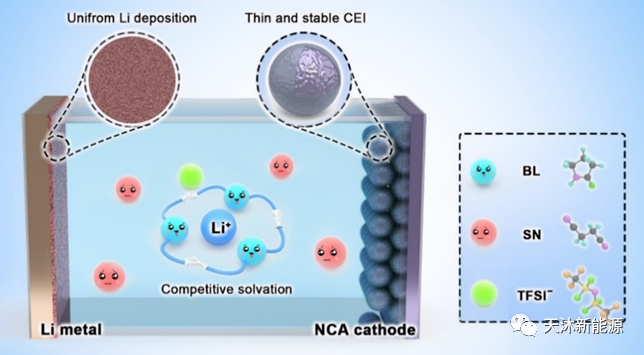
Development of ternary eutectic electrolytes offers new ideas Despite the many advantages of eutectic electrolytes, high viscosity and low ionic conductivity are the main problems that limit their application in electrochemical energy storage. Professor Jiaheng Zhang's team has designed a non-flammable ternary eutectic electrolyte and proposed a "competitive solventisation" mechanism to reduce the viscosity of the electrolyte and improve the conductivity and stability of the eutectic electrolyte (Figure 3). Benefiting from the advantageous properties of the ternary eutectic electrolyte, the assembled cells exhibit excellent cycling performance and high coulombic efficiency even under demanding conditions such as high current density, low and high temperatures. This research provides insights into the understanding and design of better electrolytes for lithium metal batteries and similar sodium/potassium metal batteries. The related research results were published in the top international journal ACS Nano (impact factor 18.03). Wanbao Wu, a PhD student at HUST, co-founder of Tianmu and chief R&D of Tianmu, is the first author of the paper.
Copyright @ 2023 Changzhou Qian Mu New Energy Co., Ltd. 备案号:苏ICP备2023016009号-1
网站建设:联动网络